Demo
Run a full diracx demo
This will allow you to run a demo setup.
The code changes will be reflected in the demo.
Requirement: docker, internet
# Clone the diracx repository
git clone git@github.com:DIRACGrid/diracx.git
# Clone the diracx-chart repository
git clone git@github.com:DIRACGrid/diracx-charts.git
# Run the demo
diracx-charts/run_demo.sh diracx/
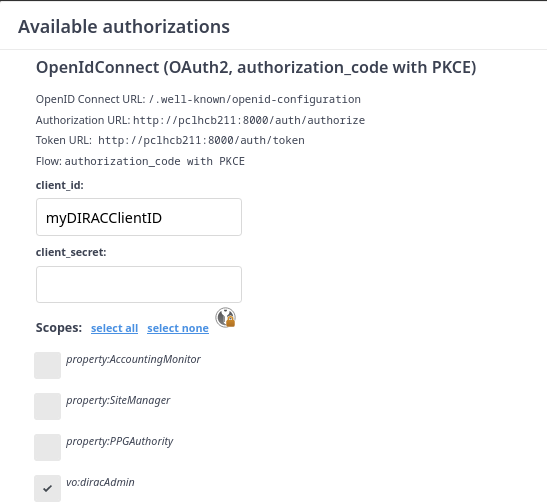
To login, click the authorize button
Connect using the authorization code flow, ticking the "vo:diracAdmin" scope
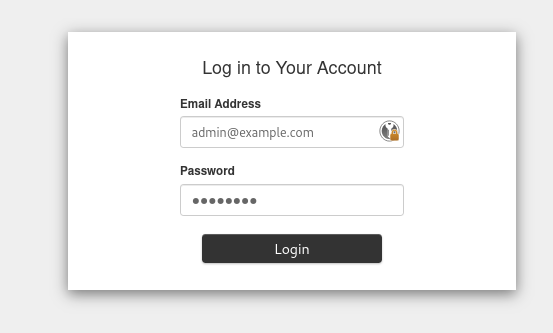
And enter the credentials prompted by the run_demo.sh script in the Dex interface
Create the dev environment
This will help you setup a dev environment to run the unit tests
Requirements: conda, git
# Clone the diracx repository
git clone git@github.com:DIRACGrid/diracx.git
cd diracx
# Create the mamba environment
mamba env create --file environment.yml
conda activate diracx-dev
# Make an editable installation of diracx
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
# Install the patched DIRAC version
pip install git+https://github.com/DIRACGrid/DIRAC.git@integration
# Enable pre-commit
mamba install pre-commit
pre-commit install
Run the test
Run the unit tests:
# In the `diracx` folder
pytest
mypy
pre-commit run --all-files
Some tests require the DiracX demo instance to be running (see above) and are skipped by default.
To enable these tests pass --demo-dir like so:
pytest --demo-dir=../diracx-charts/
Run a local instance of diracx
This only runs the diracx server, not any dependency like external IdP.
# In the `diracx` folder
./run_local.sh
Add a DB
Database classes live in src/diracx/db/<dbname>. Have a look at the src/diracx/db/dummy/ to see how to implement your own DB
- We do not want to use the
ORMpart ofSQLAlchemy(only thecore) for performance reasons
Dependency injection
Dependencies to routes on services are injected as function parameters. See the FastAPI documentation for details.
In DiracX we have a few additional dependencies which can be injected like so:
@router.get("/dummy")
def my_route(
config: Annotated[Config, Depends(ConfigSource.create)],
settings: Annotated[AuthSettings, Depends(AuthSettings.create)],
job_db: Annotated[JobDB, Depends(JobDB.transaction)],
user_info: Annotated[UserInfo, Depends(verify_dirac_token)],
) -> MyReturnType:
...
Configuration
The config object is an instance of the config model schema for the current service (e.g. diracx.core.config.Config).
This object is immutable and remains constant for the duration of the function call.
Caching is handled externally to services.
Settings
Unlike in DIRAC, DiracX separates some information from the "Configuration" (e.g. secrets).
To access this information you depend on the SettingsClass.create method which returns a cached instance of the given class.
Databases
The job_db object is an instance of the given db (e.g. JobDB).
A single transaction is used for the duration of the request and it is automatically committed when the function returns.
If an exception is raised the transaction is rolled back.
Connections are pooled between requests.
User information
The user_info object contains validation information about the current user, extracted from the authorization header of the request.
See the UserInfo class for the available properties.
Adding a router
To add a router there are two steps:
- Create a module in
diracx.routersfor the given service. - Add an entry to the
diracx.servicesentrypoint. - Do not forget the Access Policy (see chapter lower down)
We'll now make a /parking/ router which contains information store in the DummyDB.
Creating the router submodule
TODO: This isn't yet documented here however see diracx.routers.auth.well_known for an example.
Defining the new router in the diracx.services entrypoint
Modify the package's setup.cfg
[options.entry_points]
diracx.services =
parking = diracx.routers.parking:router
This will prefix the routes with /parking/ and mark them with the "parking" tag in the OpenAPI spec.
Any modification in the setup.cfg requires to re-install install diracx, even if it is a developer installation (pip install -e)
Conventions
Coding style
Most style are enforced with the pre-commit hooks which automatically reformat the code and sort the imports. Code should follow PEP-8, particularly for naming conventions as these aren't modified by the pre-commit hooks.
Import style
In addition to the automatic sorting
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone
import pytest